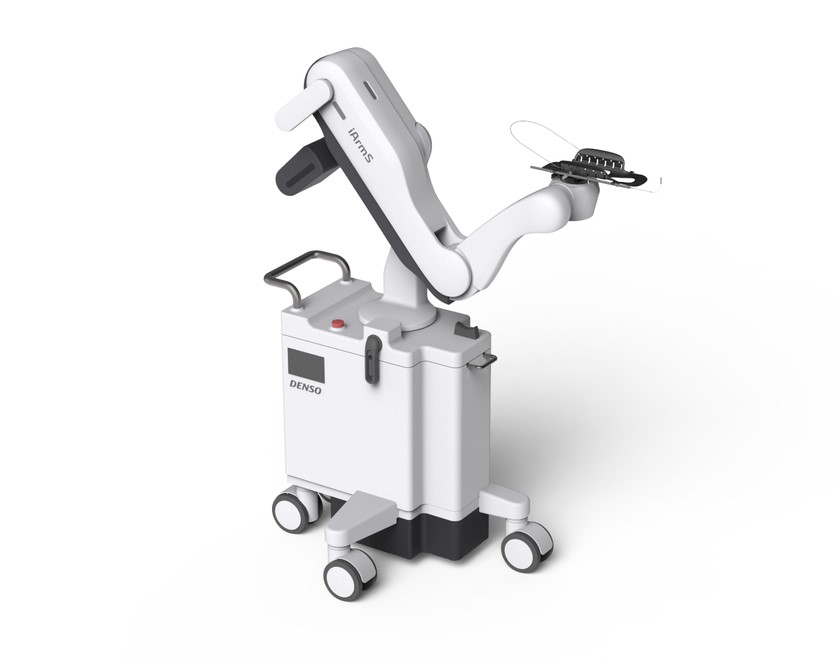
iArmS® is a surgical support robot that supports the doctor’s arm during surgery and reduces physiological hand shake and fatigue. The built-in sensor senses the actions of “putting the arm”, “stilling the arm” and “lifting the arm”. Based on this sensor information, iArmS switches between the three actions “Hold: Fixing the arm during surgery”, “Free: Moving the arm”, and “Wait: Waiting when operating peripheral devices” without any switches, allowing the operator to perform intuitive operations. The robot arm freely follows the position where the doctor wants to move the arm, and is firmly fixed during the operation to support the doctor’s arm. In order to achieve the high safety and light operability required in the medical field, the movement is performed by voluntary arm movement without using a motor. Since 2012, it has been developed jointly with Shinshu University and Denso Corporation, and has been commercialized as a result of collaboration activities involving medical doctors and engineers.

Sonodynamic therapy against cancer with a combination of ultrasound and drug
Sonodynamic therapy (SDT) combining ultrasound and anticancer drugs is being developed as a new cancer treatment. To implement SDT, an anticancer micelle containing epirubicin (NC-6300) is administered to accumulate the drug in the affected area, and 24 h after, high intensity focused ultrasound (HIFU) is irradiated to the targeted cancer. In SDT, cancer can be defeated by active oxygen species (ROS) generated from the interaction between the sonosensitizer and ultrasound. SDT is considered as a safer method because of its low-dose drug and low-energy HIFU irradiation compared to conventional single therapies. In 2017, a clinical study was conducted at Tokyo Medical University to confirm the safety od SDT, and SDT was performed on 12 patients with unresectable intractable cancer. Currently, we are preparing for further clinical trials. This research was conducted in collaboration with Tokyo Medical University, Kowa Company, Tohoku University, Tottori University, Hitachi, and DENSO Corporation.
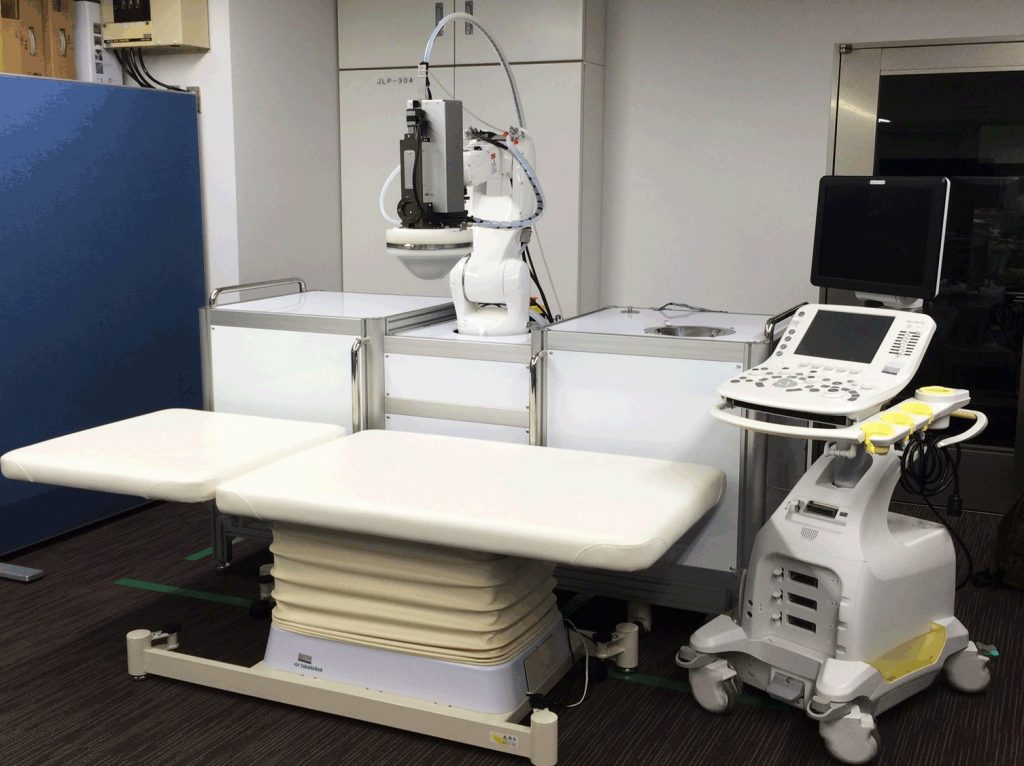
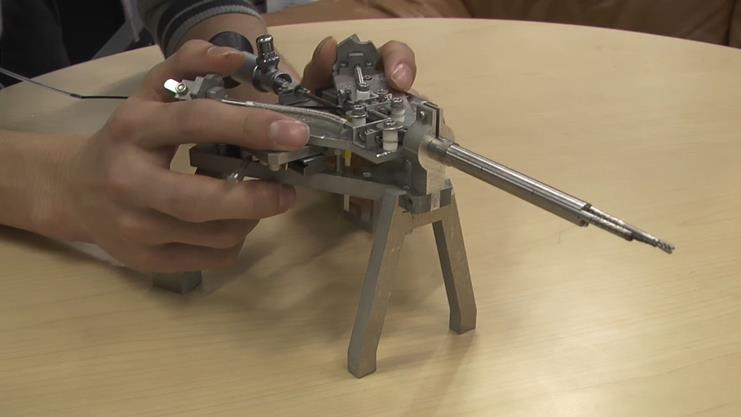
We are studying about advanced therapeutic robotics researches under a strong medical-engineering collaboration, including a robotic surgical microscope, a robotic bed, fluorescence measurement and laser treatment integrated robot systems, and scrub nurse robots. A thoracoscopic surgical supporting device solves the problem that the port position of surgical instrument is restricted by costal bones. The proposed surgical device can be set to arbitrary place by the concept of virtual incision. Surgical device for bladder tumor removal has two small bending forceps and an endoscope which are integrated in a 9 mm diameter cylinder. With the two arms, reliable removal of tumor is realized.

Information infrastructure system using artificial intelligence
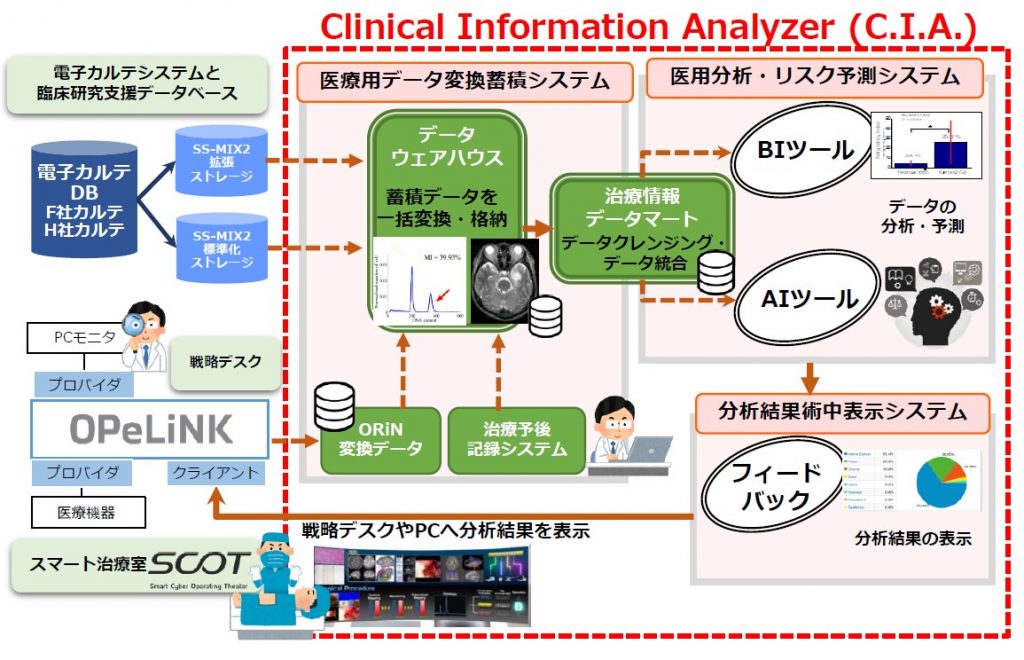
Medical information related to patient care includes not only electronic medical record information, but also surgical information, vital data, and rehabilitation information. Therefore, we are developing an information infrastructure system for analyzing medical information data including electronic medical record systems and medical device data collected in intelligent operating rooms and smart treatment rooms. Furthermore, a clinical information analysis system for quickly predicting the survival and functional prognosis of glioma patients, prediction of intraoperative risk, and advice on improving surgical efficiency using the artificial intelligence. By developing the system, ‘Future Prediction Surgery’ will be realized. This research and development was conducted in collaboration with Hitachi, Ltd., Waseda University, and Future University Hakodate.